
The microbubbles can be seen filling the arterial lumen 30 seconds after the injection. When necessary, the dose was modified according to the body type of the patient’s neck and was increased to as much as 4.8 mL. The contrast agent dose used was 2.4 mL administered with an intravenous fast bolus injection and followed by normal saline infusion through a three-way stopcock.

US contrast agents are based on microbubbles measuring approximately 1-8 μm, which are filled with a perfluorinated gas and covered with a phospholipid or protein shell. The CEUS examination was performed after intravenous administration of the SonoVue (Bracco SpA, Milan, Italy) contrast agent and was mainly used to either accurately define the stenosis grade, identify plaque ulcerations or neovascularization. During the last year, we performed a complementary CEUS examination of selected patients where the conventional techniques could not fully evaluate the extent of atherosclerotic disease. All the examinations were performed with an Aloka Prosound alpha 7 device (Aloka GmbH, Meerbusch, Germany), with a 5-13 MHz linear array transducer. It is used to more accurately delineate the borders of the plaque and to image highly stenotic parts, avoiding the overwriting artifact of the conventional color Doppler technique. The D-eFLOW technique is a new high-definition blood flow imaging technique that is characterized by increased spatial and temporal resolution and is available in some US devices.
CAROTID DOPPLER RADIOLOGY FREE
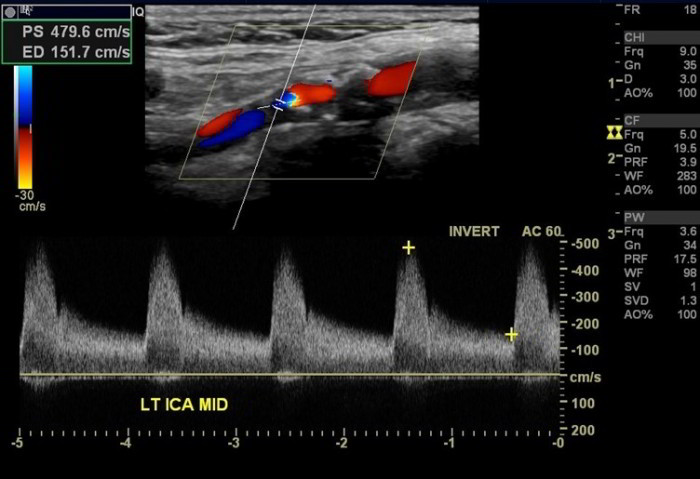
PDI is used as a technique to better delineate the plaque surface and the slow flow as it is more sensitive than color Doppler and free of the aliasing artifact. PW Doppler is used to measure prestenotic and poststenotic blood flow velocities and grade stenosis. It thus reveals echolucent plaques, which are undetected in the gray-scale technique, and demonstrates the blood flow pattern, highlighting stenotic areas. The color Doppler technique estimates and displays the mean velocity of red blood cells in a scanned area as a color map superimposed on the gray-scale image. Gray-scale imaging provides information about morphological structures within the vascular lumen, the vascular walls, and the surrounding tissues. The standard protocol for carotid US in our Radiology Department includes gray-scale imaging (B-mode), color Doppler ultrasonography (CDU), power Doppler imaging (PDI), pulsed-wave (PW) Doppler, and the directional-eFLOW (D-eFLOW) technique of the common, internal, external carotids and the vertebral arteries.

Our purpose is to illustrate the value of a CEUS examination. Where appropriate, we provide comparative multidetector computed tomographic angiography (MDCTA) or contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CEMRA) images. In this pictorial essay, we present selected images from the carotid US and CEUS examinations of patients with important abnormal findings. Both neovascularization and ulcerations are considered to increase the plaque’s vulnerability and predict cerebrovascular events. In addition to this, CEUS has been shown to reliably evaluate intraplaque neovascularization (IPN) and identify carotid plaque ulcerations with superior diagnostic accuracy as compared to the color Doppler technique. CEUS has been proven to more accurately visualize the arterial lumen than the color Doppler technique. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) has emerged as an improved imaging technique to detect and evaluate atherosclerotic plaques with the use of a contrast agent based on microbubbles. Ultrasonography (US) is a well-established imaging modality for evaluating carotid atherosclerotic disease, which may cause approximately a third of brain infarcts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
